Map of cystic fibrosis mechanisms
To the development of the cystic fibrosis map mechanisms the information from literature is integrated into a large-scale Activity Flow diagram. Particular focus is on a specific mutation in the CFTR gene, F508del, the most common mutation in CF patients.
Information from pathway databases is reused when possible, and contextualised.
The network is presented in the Systems Biology Graphical Notation (SBGN) standard. A community of domain experts is involved to ensure that the disease mechanisms are adequately represented.
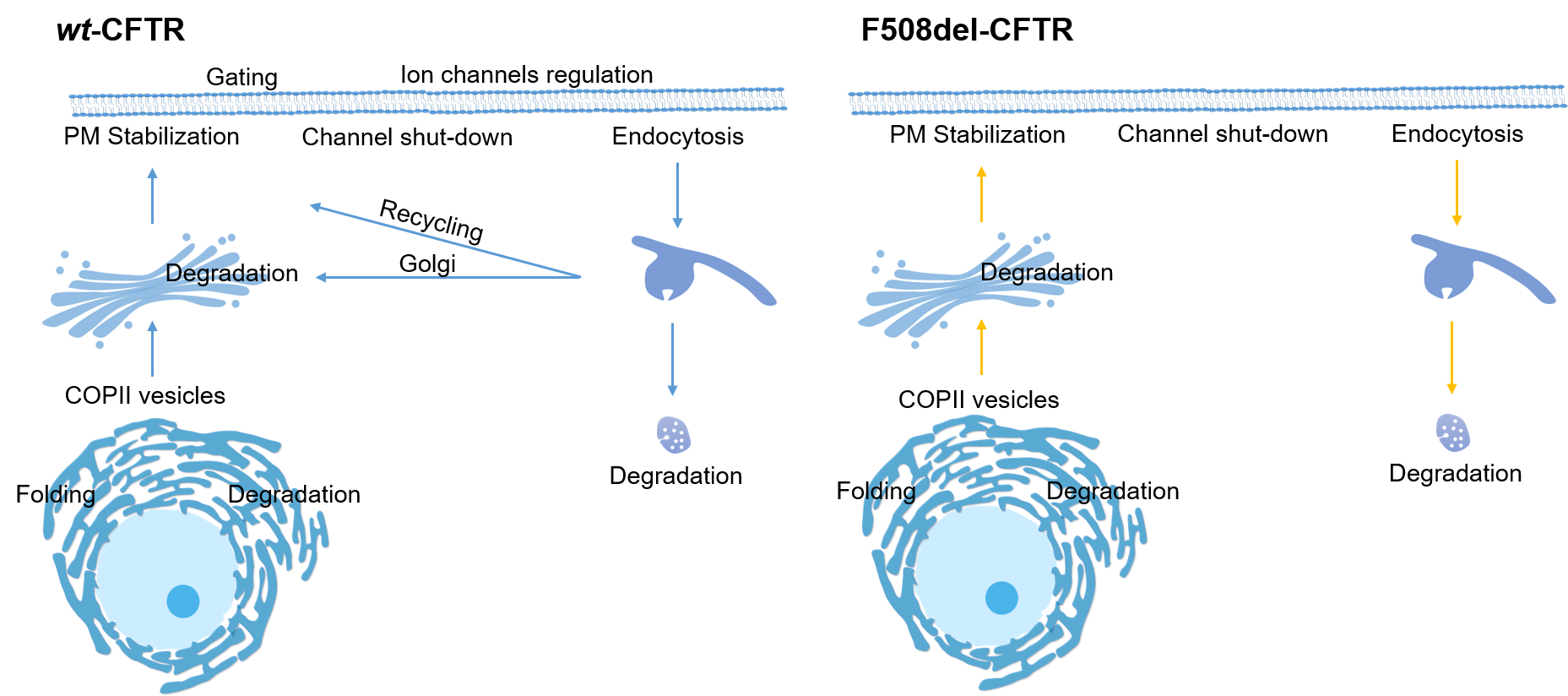
Pathway outline in SBGN Activity Flow: normal vs. F508del mutation
| wt-CFTR and F508del-CFTR |
 |
Representation of modules included on CyFi-MAP
A diagram of CFTR life cycle processes included on the map is shown. This information will be updated and continuously growing.
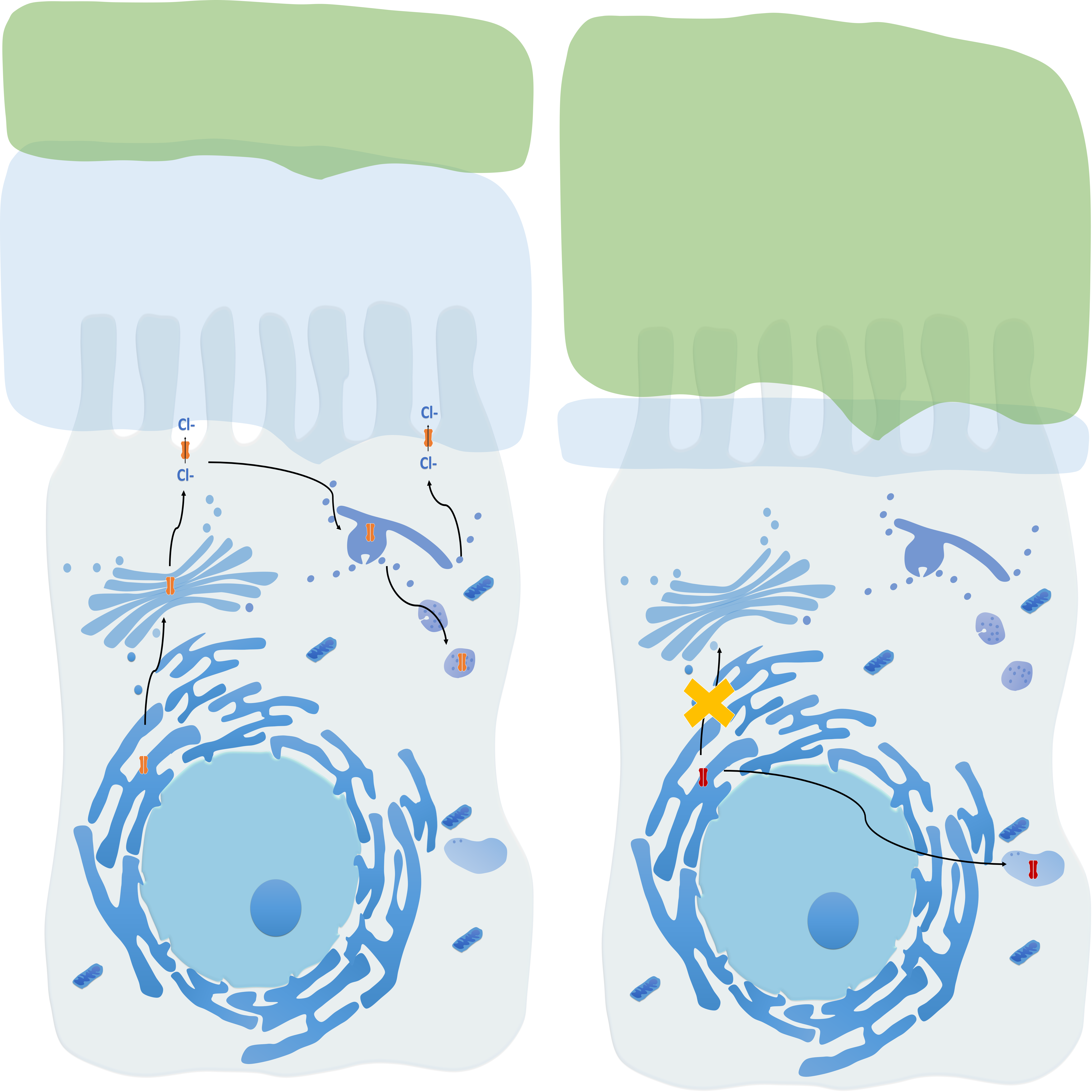
Endoplasmic Reticulum folding in wt-CFTR and F508del-CFTR
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Folding in both submaps. The four ER Quality Control checkpoints are present with wt-CFTR in blue [3], [6], [7], [8].
In F508del-CFTR submap, only the first ER Quality Control checkpoint is present with F508del-CFTR in green [2].
Plasma membrane stabilization in wt-CFTR and F508del-CFTR
Plasma membrane (PM) stabilization in both submaps. wt-CFTR in blue is delivered to the PM and stabilized with several proteins involved in its anchoring [11].
In F508del-CFTR submap, F508del-CFTR appear in red because it is rescue through low temperature or chemical compounds. Proteins in yellow bind exclusively F508del-CFTR [5].
Recycling/Degradation at sorting endosome in wt-CFTR and F508del-CFTR
Sorting endosome in both submaps. wt-CFTR is represented being recycled through different pathways, either directly to the PM [22], [23] or through Golgi [24], and being degraded [25].
F508del-CFTR is characterized by not being recycled, represented only in a degradation pathway with several extra proteins assisting [10].





